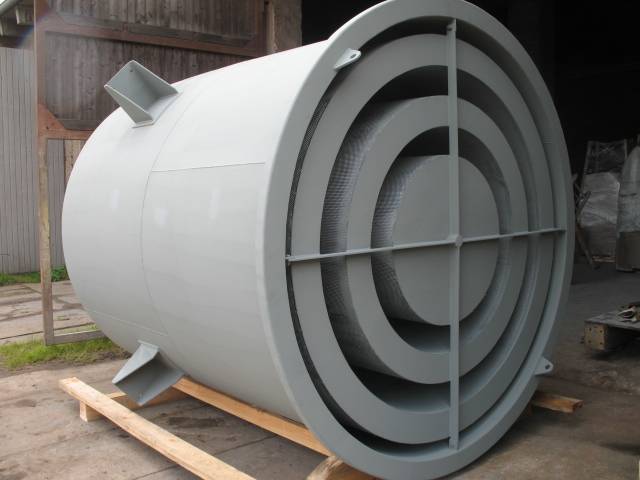
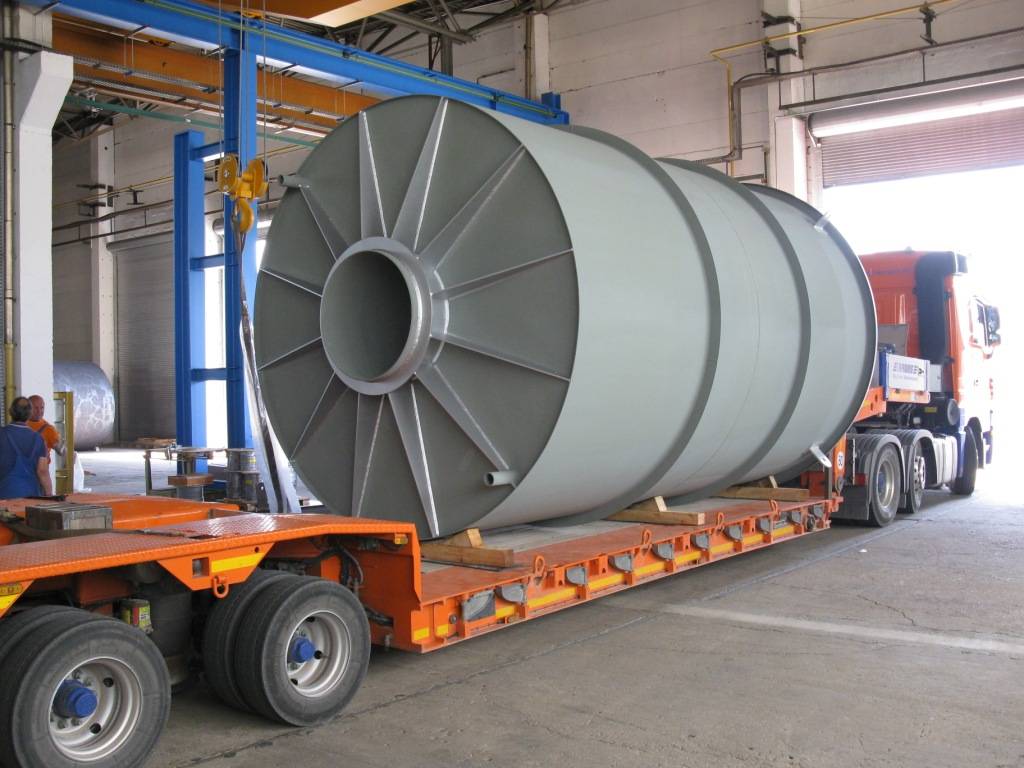
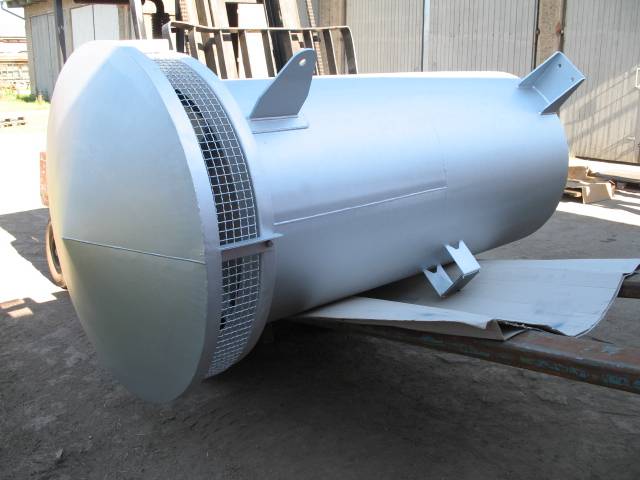



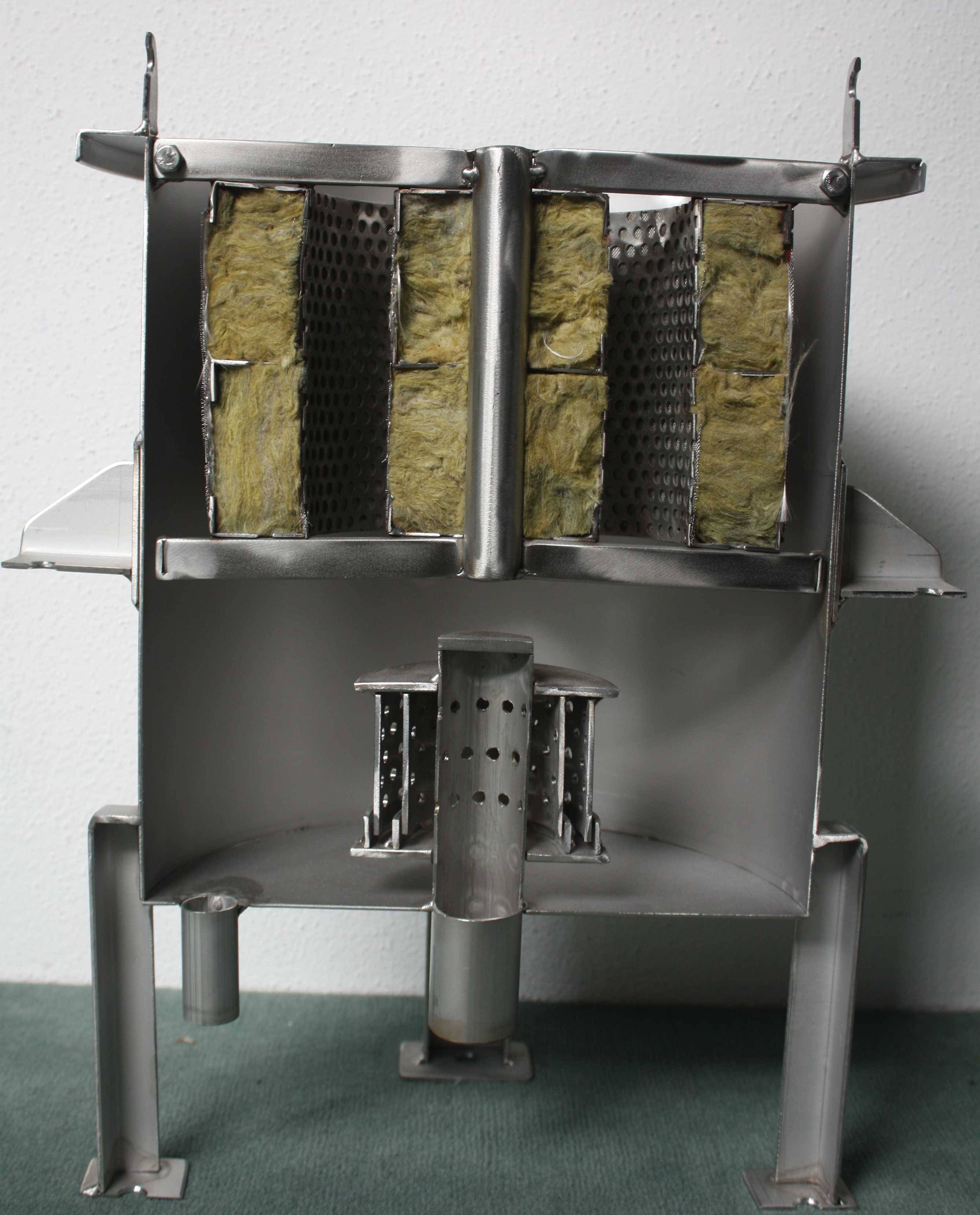
Use of blow-off silencers with / without pressure relief stages
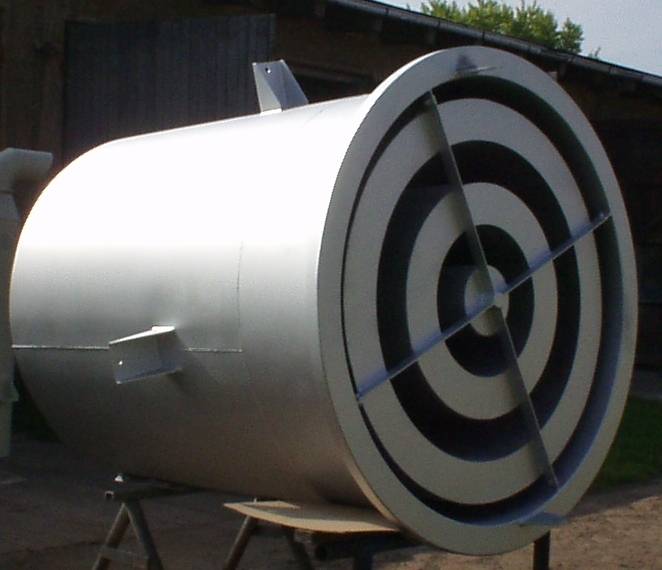


• Gas- or steam flow
• Temperature and pressure upstream (before) valve
• permissible sound pressure level at immission point (in defined distance), e.g. 85 dB(A) in 1m distance
• diameter of inlet nozzle (if defined)
Note: At blow off silencers for safety valves the allowable back pressure caused by the expansion orifice depends on the construction of the valve. Most safety valve manufacturer allows a maximum backpressure of 15% of the set pressure. This allowable backpressure should be utilised because of the following reasons: 1.) the differential pressure over the valve is lower, 2.) piping behind the valve could be designed at smaller size, 3.) the silencer could be designed at optimal cost.
To clean pressure steam pipes for HRSGs or turbines during commissioning of a plant high pressure steam is used for blowing out the pipe with preferably a high velocity of steam.
To reduce the noise at the opening of the pipe blow our silencers are used. The differences to a blow off silencers are as follows:
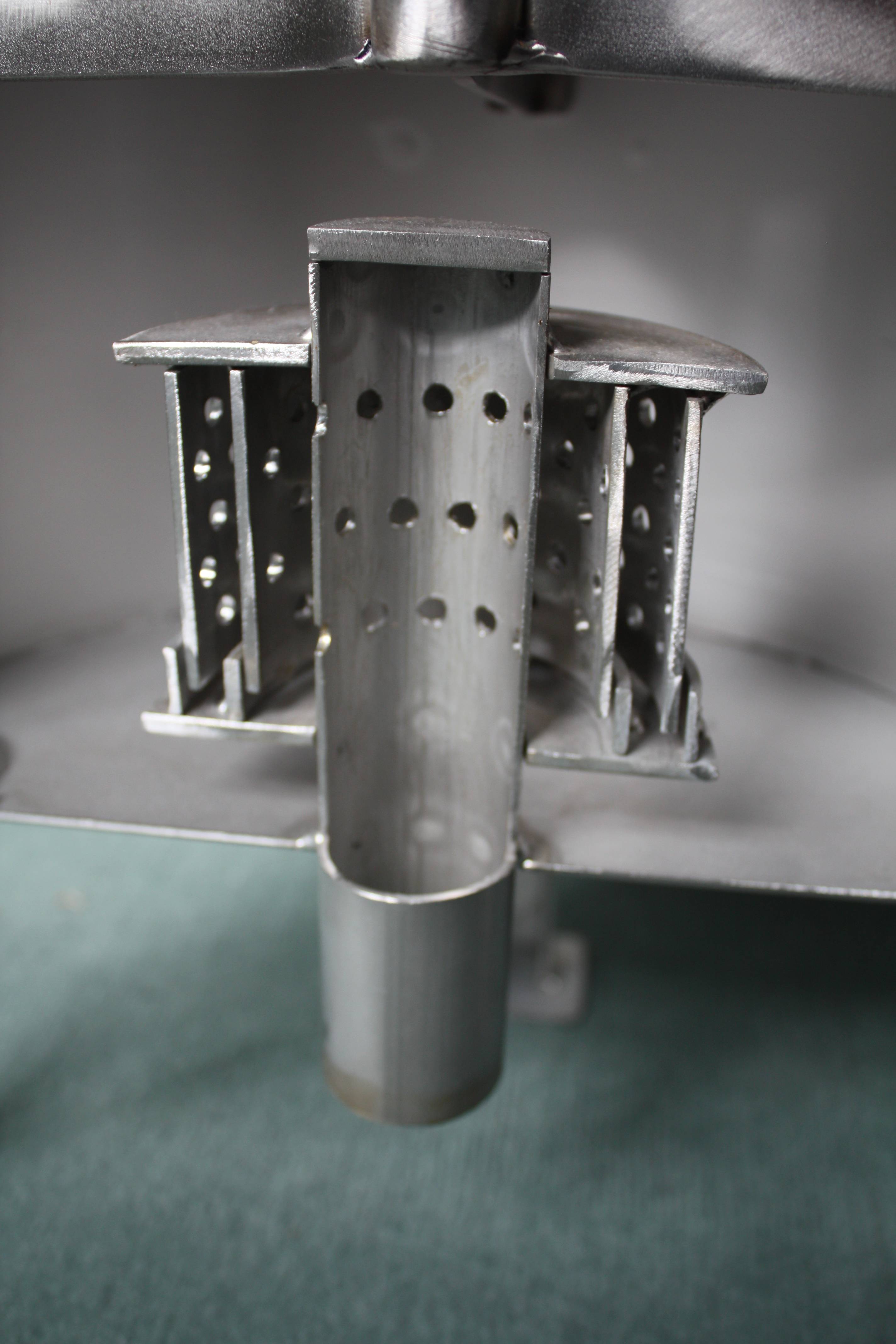
1. expansion system in the silencer designed for maximum flow velocity in the line
2. preferably without absorption baffles (size)
3. removable pressure reducer (exchange, repair)

If the boiler is designed to 40 bar / 450 °C, the blow out pipe should be cleaned acc. to VGB directive with approx. 20 – 25 bar / 400°C.
If the valve (slide valve) is opened during short time of e.g. 10 seconds a steam mass flow is generated total independent from the performance of the HRSG. The resulting mass flow is depending from the pressure drop of the outlet system and the Cv value of the valve.
By experience, calculations and measurements at several plants a mass flow in this case will be about 100 to 129 tons per hour for duration time of 10min. (Base: pipe size 8”)
Silencer for rental:
For 1-time blow out cases you can rent a silencer from us. The Rentalsilencer can be connected with a NPS 12“ nozzle. The rental fee contains the overhaul in our shop after usage and if necessary the repair work – incl. ultrasonic or X-Ray testing of the critical welding lines.


